In 2014, it was Stephen Hawking who said that the “development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end for the human race.” There is perhaps no single place where this observation is more applicable than in the military use of AI. Equipping highly autonomous machines with deadly weapon systems has raised a serious discussion about the future of warfare and the human race
In the past, these were armaments that were rarely used in the vicinity of civilian or civilian objects, but a worrying interest has emerged in its use against humans directly. As the development of Lethal Autonomous Weapon Systems (LAWS) progresses, several concerns have been brought up about the risks associated with these newly emerging technologies in this area. This article seeks to explore these concerns. In particular, it argues that the use of AI in warfare will lead to an increase in human casualties.
To briefly provide some context, autonomous weapons, as they are defined in this article, refer to “any weapons that select and apply force to targets without human intervention”, according to the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC). When activated, they collect information from the environment through sensors and match them against a target they have learned to identify. They receive their autonomy from the fact that the weapon has the freedom to make the final call on whether to strike an identified target or not. Many nations have already pushed back on the employment of such weapons and the debate around their use grows only larger.
Problems of Predictability
As LAWS continue to develop their ability for complex decision-making, the risk of their unpredictability rises. The rigid set of computational rules that they are required to operate under start to blur as they are given more freedom to perform more actions at any given time. A 2014 ICRC report supports this claim, stating that “increasing autonomy – and less strictly defined rules – there will be increasing uncertainty about how the system will operate.” This raises concerns about the reliability of these machines, as their unpredictability may cause accidents that have deadly consequences, especially those equipped with lethal weapon systems.
The resulting lack of predictability of LAWS means that verifying and validating their behaviour in a suitable environment becomes very challenging. A 2020 study performed by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University found that testing for the outcomes of all the potential actions an autonomous agent can take is one of the primary challenges in autonomy testing. They explain that the number of possible test cases can increase rapidly given the number of inputs the machine has to deal and the number of actions it can perform. As a result, the difficulty of constructing a robust and complete testing environment explodes once a robot is given a task that involves operating in highly complex conditions.
Is there a way to improve predictability?
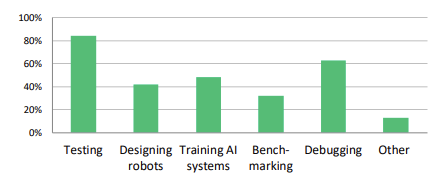
The introduction of simulations may help alleviate the issue since it provides a programmable and constrained environment in which to test a LAWS’ operation. A 2020 survey conducted at Carnegie Mellon University found that over 85% of its participants stated they use simulations as an integral tool to extensively test and build robot software. Nations such as the United States and United Kingdom are making concentrated efforts to improve simulation testing and frequently use it in their own projects.
However, this approach brings with it its own set of challenges. The simulation may suffer from a ”reality gap”, where the complexity of an autonomous machine and the environment its operating in is too difficult to recreate realistically. The non-deterministic nature of simulations also makes reproducibility of testing a challenging task. As a result, simulation testing may not yet be a suitable solution to improving predictability, especially in light of the complexity that LAWS demand.
Other measures can also be taken to improve predictability. In another report published by ICRC, the authors state that it is helpful to “constrain the environment in which the system operates.” This approach involves developing LAWS for scenarios with less environmental variables, which helps to improve predictability by narrowing down the number of inputs the machine would need to process. However, this would also limit its flexibility, since it has only been sufficiently trained on a select number of environments. If it is ever exposed to a scenario it has never seen before out in the field, it would not know how to react and could lead to an increase in lethal accidents.
The AI Arms Race
An arms race between nations is likely to occur as countries compete to acquire the latest technology and maintain an economic and military advantage. The use of LAWS gives nations the potential to have a significant advantage in warfare and military operations, and countries may feel compelled to develop and use them to remain competitive. A 2021 report published in The Strategist draws parallels to history in how the industrialization of Europe enabled the continent to become the dominant force globally. By 1900, Europe had control of 62% of the global manufacturing output and by 1914, occupied 80% of the world’s land surface. A similar scenario could unfold with the development of LAWS, where the military and economic incentives to take advantage of this technology may lead to growing global tensions.
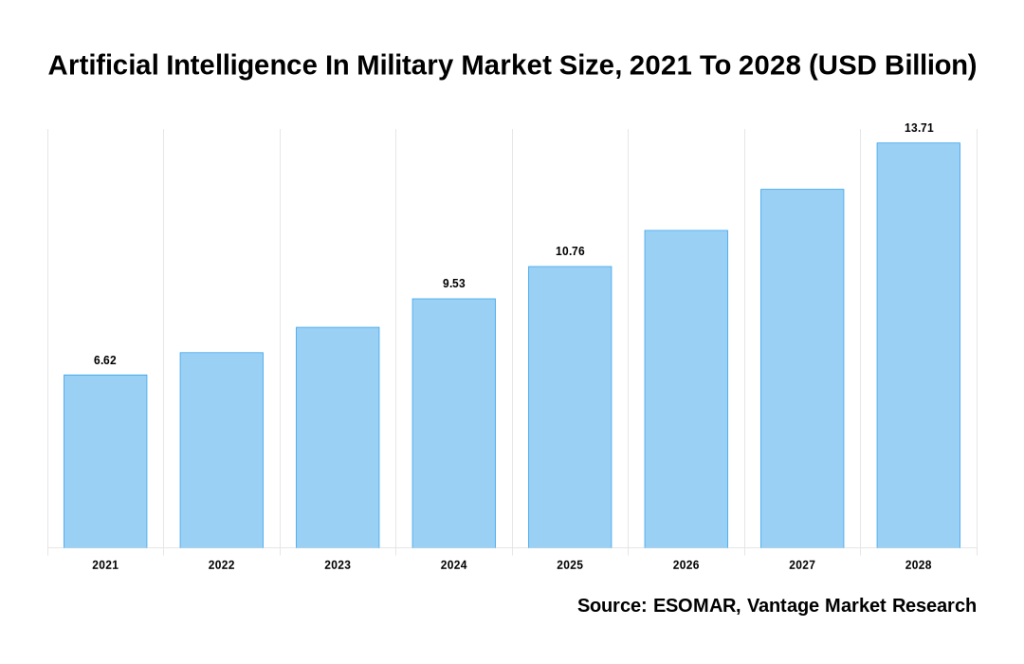
The arms race could also result in a significant increase in military spending and resources devoted to the development of LAWS, putting a strain on national economies and increasing the risk of conflict. The global revenue of AI is projected to reach approximately $13.71 billion by 2028, up from $6.62 billion in 2021.
Furthermore, since the use of LAWS help to make wars cheaper, it may become much easier for nations to wage war. Conflicts will become more accessible to small, rich nations because warfare is no longer reliant on a country’s size, but rather their wealth and resources. This may have the unfortunate consequence of spilling over into civilian deaths, especially considering that wars tend to get out of control quickly due to the increasing motivation from each side to achieve victory.
How can we approach the AI arms race?
A potential solution to the arms race over LAWS requires international cooperation and regulation. United Nations member states can come together to establish international regulations and agreement on the development and use of autonomous weapons. These agreements should ensure accountability and transparency, and limit the proliferation of these weapons. The international community can work to limit the spread of LAWS to prevent them from falling into the wrong hands. This could be achieved through arms control agreements, export controls, and other measures.
However, this solution is going to be exceedingly difficult to enforce due to the rapid improvements being made in AI every year. There are simply too many nations, companies, organizations and academics working on the technology. The human and economic costs may be very high to make sure regulations keep up with the growth. It may also be likely that the nations working on AI will pushback on regulations, which makes this path towards limiting the use of LAWS even slower.
Another solution that has been offered is that companies should perform a complete ban on the development of any autonomous weapon that may be lethal. This has been offered by the peace organization PAX, which recommends that every company establish an ethics committee to enforce this policy. However, this approach would likely have little chance of success, mainly due to the amount of economic and military interest nations around the world have already expressed in the production of LAWS.
Conclusion
The benefits that AI can bring to the world speaks for itself, but we should make sure to tread very carefully on the path towards arming them. The unpredictability of LAWS and the difficulty in appropriately testing them may lead to a loss of human life through deadly accidents. Meanwhile, the possibility of an AI arms race may lead to increased global tensions as nations feel compelled to use AI to gain a military advantage. While this article does not offer a concrete set of solutions, it is clear that how we approach this emerging technology in the coming decades will be a defining moment in the history of the human race.