Introduction
As we stand at the crossroads of technological change, the rapid development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has sparked widespread concern and worry around the world. How should we respond to this concern? Should we succumb to public panic and impose various restrictions on the development of AI, or should we bravely remove obstacles and promote further development of AI technology? This is not just a technical issue but also a major decision about the future development path. Especially for a region like Europe, which holds a key position in global scientific and technological competition, this decision is even more crucial.
Stating Supporting Views
Generalized Technological Potential of AI
AI is widely recognized as a transformative General-Purpose Technology (GPT) with game-changing potential. As Crafts (2021) points out in his study, the core value of AI as a GPT lies in its ability to “invent new ways of inventing,” thus increasing the productivity of R&D in the long run. Since artificial intelligence is potentially a general-purpose technology that raises the productivity of research and development, it may be the foundation for a Fourth Industrial Revolution.
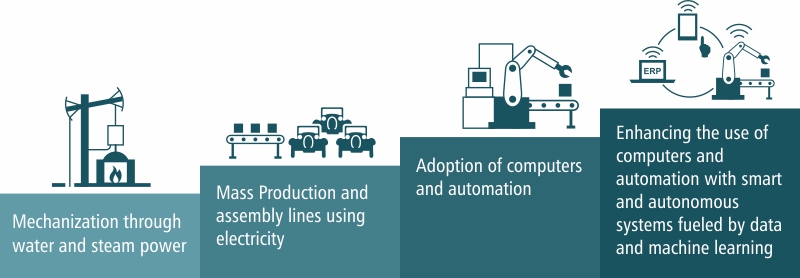
Historically, every technological revolution has initially been modest in its productivity gains. However, as the technology matures and its applications expand, its full impact on the economy and society will become increasingly significant.
Positive Impacts of AI on Society
The development of AI heralds the liberation of humans from repetitive and low-value-added labor. Bankins and Formosa’s (2023) study highlights the potential of AI to give more meaning to work, especially by automating tasks that are tedious and repetitive. This could not only increase labor efficiency but also enable humans to focus on more creative and strategic work, thus contributing to the overall well-being of society.

Furthermore, the development of AI can bridge the gap in high-value-added services previously limited by a lack of skilled professionals. For instance, in healthcare, the application of AI is revolutionizing our approach to healthcare. As Alowais et al. point out in their 2023 study published in BMC Medical Education, AI’s role in healthcare far exceeds simple task automation. The development of AI has significantly improved the quality of patient care by providing powerful support for diagnosing diseases, developing personalized treatment plans, and assisting clinicians in decision-making.
Geopolitical Perspective
Limiting the development of AI could weaken Europe’s position in global tech competition. The United States and China currently lead in AI technology development, partly due to their large, single-language digital markets and relatively few taxes and restrictions on their tech industries. China, in particular, benefits from government orders and subsidies as positive incentives and has almost non-existent personal privacy protection. As Brattberg et al. (2020) describe, Europe possesses a strong industrial base and research capabilities in AI, but over-regulation may hamper its pace of innovation and commercialization.
Rebuttal to Objections
Labor Market Adjustments
While AI may impact the traditional labor market, these changes can be mitigated by policy adjustments. For instance, introducing Universal Basic Income (UBI) and other changes in distribution mechanisms can mitigate short-term unemployment caused by automation and stimulate new economic activities and job creation. According to Crafts (2021), policies to reduce adjustment costs and facilitate the redeployment of workers will be important in supporting effects that can offset the initial displacement effects caused by automation.
AI and Energy Consumption
AI may indeed increase energy consumption, but the benefits it produces are likely to far outweigh its consumption. Historically, the core of the first and second industrial revolutions was centered on revolutions in energy technology, suggesting that the next industrial revolution may follow a similar paradigm, such as controlled fusion. The development of AI will accelerate this process, potentially yielding greater green benefits in the future. Mohammad and Mahjabeen’s (2023) study shows that AI plays a key role in fostering the development of renewable energy technologies, particularly in the field of solar energy. AI not only improves the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar energy systems but also aids in the transition to a more sustainable energy system.

Conclusion
Europe must remain steadfast in its support for the development of AI. By further removing barriers to AI development, promoting necessary infrastructure, and advancing a unified digital market, Europe can ensure its competitiveness in the global AI industry. Moderate and prudent policy support, mindful of the social and ethical implications of technology, will enable Europe to seize opportunities in the new technological revolution while ensuring that technological development aligns with its values and long-term interests. Liberating artificial intelligence will bring unprecedented opportunities and benefits to both Europe and global society. In the exhilarating wave of AI technology, Europe should lead, not follow, actively embracing this change and giving wings to the future development of the global community.

