The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) presents a dual-edged sword, offering unprecedented opportunities while introducing complex challenges, particularly in the realm of digital security. At the heart of these challenges is the pressing need for effective internet identification systems capable of distinguishing between human and AI interactions. We will explore the vital importance of such systems, emphasizing their role in bolstering security, protecting democratic values, and addressing privacy concerns. It also sheds light on the potential risks and obstacles involved. The development of a secure internet identification system that honors privacy and democratic principles requires a concerted effort from policymakers, technology companies, and the general public.
Enhanced Security
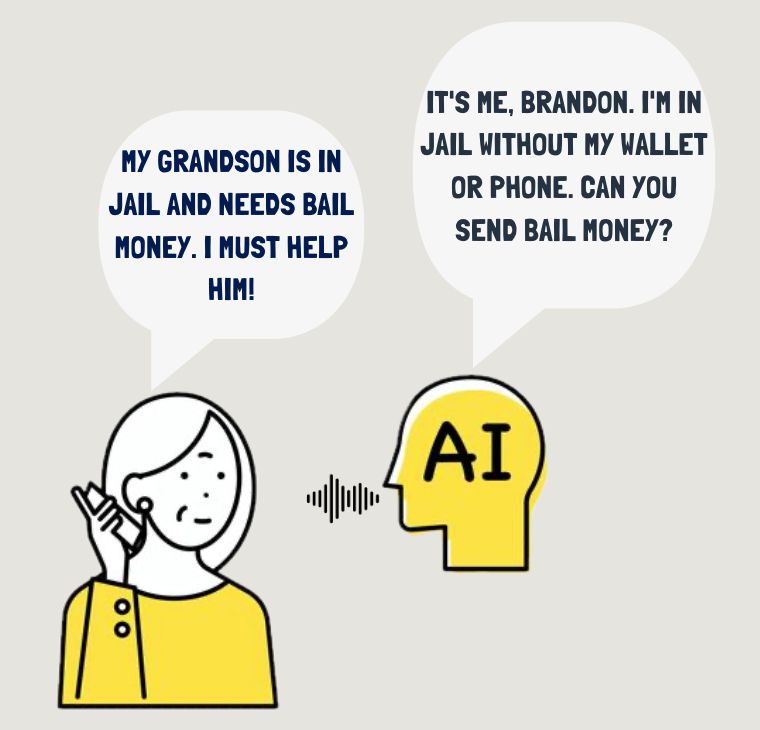
The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly heightened security concerns, especially in the area of identity theft. AI’s ability to imitate human behaviors and circumvent traditional security protocols has led to a surge in AI-enabled fraud and synthetic identity fraud. These types of fraud often involve creating convincing, deceptive content or generating new identities by blending real and fabricated information. Against this backdrop, the concept of Proof of Personhood (PoP) stands out as a powerful countermeasure. Serving as a foundational element for digital identity, PoP ensures that each person can only create a limited number of accounts, providing a solid defense against sybil attacks. This limitation proves particularly effective in combating AI-driven and synthetic fraud. Additionally, the emergence of voice AI technologies, which allow fraudsters to replicate the voices of trusted individuals, introduces a novel challenge. Nonetheless, by verifying that an identity is exclusively used by its rightful owner, PoP can significantly contribute to thwarting such impersonation attempts. As AI technologies advance, these security challenges are likely to escalate, highlighting the critical role of PoP in preserving the integrity of our digital ecosystem.
Safeguarding democracy
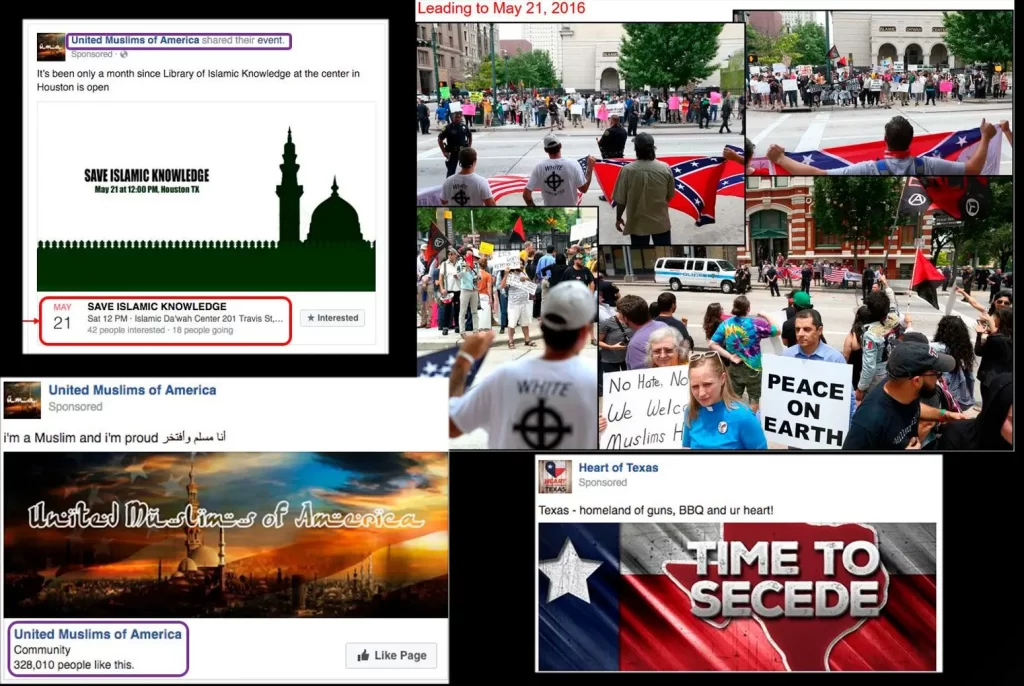
As evident, AI is currently employed to manipulate individuals. However, what raises greater concern is the potential for AI models to manipulate large populations simultaneously. An illustrative example occurred in 2017 in Houston, Texas, where malevolent actors from Russia established two Facebook groups: ‘Heart of Texas’ and ‘United Muslims of America.’ Through advertising and the efforts of group administrators, these groups amassed a significant number of followers, who were then targeted with posts about upcoming rallies. The Heart of Texas group members were prompted to attend the ‘Stop Islamification of Texas,’ while the United Muslims of America group members were encouraged to participate in a ‘Save Islamic Knowledge’ rally. These events coincided in both time and location, leading to confrontations and verbal attacks. Only after investigators discovered that none of the protest organizers were present did they realize the rallies were the result of a Russian manipulation campaign. While the effort of a few individuals was adequate to incite violence, it still demanded considerable work. Now, envision a scenario where, instead of traditional advertising and content curation by individuals, an AI model impersonates numerous people and generates thousands of social media posts designed to sway public opinion. Such tools could be wielded to influence democratic elections on an unprecedented scale, surpassing the combined impact of radio and TV.
Manipulating elections and inciting violence represent just a fraction of the potential dangers posed by AI. Language models (LLMs) could be employed by private companies to fabricate product reviews or, more nefariously, to conceal misdeeds through specialized PR campaigns. This underscores our belief in the necessity for a form of proof of personhood to distinguish genuine individuals from AI-driven bots on the internet. While we currently grapple with issues like spam bots on platforms such as Twitter and Facebook, the advent of AI will only exacerbate the difficulty of identification.
AI models also appear to validate the Dead Internet theory, suggesting that if there are no reliable means to identify genuine users, the Internet may lose its allure as a communication medium. More crucially, it may stagnate without the infusion of new and meaningful information. Secure and verifiable digital identities are paramount in protecting elections from undue influence and preserving the integrity of democratic discourse. Internet digital IDs are instrumental ain ensuring that every voice heard is authentic and every vote counted is legitimate, thereby safeguarding democracy against the manipulative capabilities of AI.
Privacy concerns
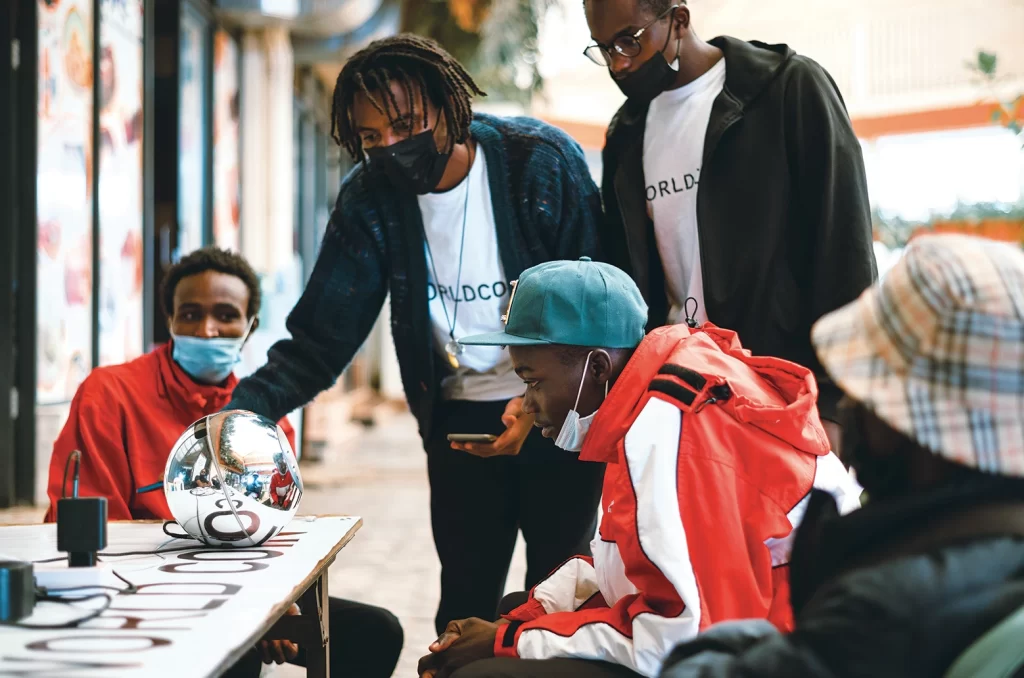

The implementation of internet IDs, while undeniably advantageous in enhancing security and safeguarding democracy, gives rise to substantial privacy concerns. Initiatives like Worldcoin, which involve the collection and retention of personal data, underscore the potential for overreach and surveillance. This apprehension raises a critical question: should AI companies profit from a problem they played a role in exacerbating?
It is imperative to highlight that data leaks of such sensitive information could empower malicious actors to track individuals’ internet activities with significantly fewer resources than government agencies use for threat detection. If internet IDs contain more than just proof of personhood, granting control over such data to private entities becomes concerning. Simultaneously, strict constraints on governmental use of internet IDs are essential, considering leaks from whistleblowers have exposed instances of abuse of power.
We acknowledge these concerns and underscores the necessity of prioritizing privacy. One key recommendation is the implementation of robust measures such as data encryption. Balancing the need for enhanced security with the protection of individual privacy requires crafting systems that prevent authoritarian control. Achieving this delicate balance is a complex challenge, underscoring the need for stringent regulations governing digital identification and ethical data practices.
A balanced approach
Navigating the complex landscape of security, democracy, and privacy in the AI era necessitates a multifaceted and balanced strategy. This strategy should encompass the development and enforcement of rigorous digital identification regulations, a commitment to ethical data handling practices, and a steadfast dedication to transparency. A concerted effort from policymakers, technology companies, and the public is imperative to forge a system that not only enhances security but also staunchly defends privacy and democratic values.
To illustrate, the adoption of decentralized identity systems can empower individuals with greater control over their personal data, leveraging blockchain’s robust security features to safeguard against unauthorized access. Incorporating privacy-preserving technologies, such as zero-knowledge proofs, further ensures that individuals can verify their identities without compromising sensitive information, striking a crucial balance between privacy and security. Moreover, the widespread implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) across digital platforms significantly bolsters security defenses, making it considerably more challenging for malicious actors to exploit identities.
In parallel, the establishment of ethical guidelines for AI development is critical. These guidelines should prioritize transparency, auditability, and the prevention of AI’s misuse in political manipulation, thereby protecting the integrity of democratic processes. Additionally, enhancing public awareness and education on digital literacy and cybersecurity can equip citizens with the knowledge needed to navigate the digital realm safely and responsibly.
Regulatory oversight plays a pivotal role in holding tech companies accountable for the privacy and security implications of their products. This includes establishing clear penalties for data breaches and the misuse of personal data, as well as ensuring that AI technologies are deployed in a manner that respects democratic engagement and individual privacy.
Lastly, in an era where digital threats transcend national boundaries, international cooperation is essential. Collaborating to set global standards for digital identification, privacy, and AI ethics will help unify efforts to secure democracy and privacy in the digital age.
By embracing these directions and integrating the aforementioned examples into our approach, we can collectively address the challenges posed by AI with thoughtfulness and cooperation. This will enable us to cultivate a digital environment that is not only secure and democratic but also deeply respectful of privacy.

The path to a secure digital future in the AI era is laden with challenges but also brimming with opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Through careful regulation and thoughtful implementation of internet identification systems, we can navigate the complexities of this new era. Such systems must strike a delicate balance between the imperative for security and the need for privacy, addressing the challenges introduced by AI while preserving democratic values and individual privacy. By uniting all stakeholders in a concerted effort, we can develop a digital landscape that effectively safeguards against malicious AI activities and fosters a safe, secure, and democratic digital domain.


