In an era of digital interconnectedness, the symbiotic relationship between social media and Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed the way we communicate, share, and experience the world. As we scroll through our feeds and interact with tailored content, an intricate web of algorithms powered by AI is silently at work, shaping our digital reality. However, the personalized experience overshadows a major concern for the general masses, the erosion of privacy.
Welcome to our opinion article which delves deeper into this intricate and often perilous intersection of Social Media and AI. Through this article we shall try to discuss why this technological marriage is not as unharmful as it seems, particularly when it comes to safeguarding one of mankind’s most intimate asset – our privacy. From data exploitation and algorithmic biases to invasive personalization and the shadows of surveillance capitalism, we embark on a journey to unravel the complexities that render Social Media and AI a potential threat to the sanctity of our private lives.
Join us as we navigate this privacy minefield, peeling back the layers to examine the darker implications of the seamless integration of Social Media and AI. It’s time to confront the uncomfortable truths and engage in a critical discourse about the risks posed to our privacy in the age of digital connectivity.

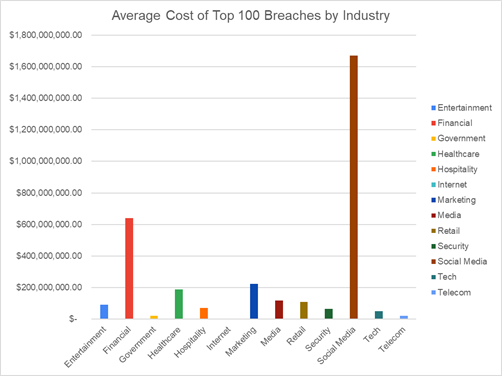
AI systems are largely dependent on extensive-scale datasets, which contain information about individuals handled through different methods. These methods are often opaque and require secure storage, especially when stored for long periods, making them susceptible to cyber-attacks and data breaches [1]. This data breach susceptibility is not only in theory, but has also been exploited repeatedly in the past leading to major financial as well as personal data loss. “We looked at mega-breach impact across industries and found that social media data breaches, specifically those involving Facebook were the most common. Social media breaches were 20% of mega-breaches and Facebook or developers of Facebook applications made up 7% of mega-breaches” [2]. The report further found out that social media companies had the highest costs on average for data breaches between 2004 and 2020, as visualized below.
Focusing on the role of AI in social media, its implementation involves studying user behavior and engagement. The goal of AI here is to improve content creation, user interactions, and facilitate data-supported decision-making. The aim is to deliver a social media platform that is efficient, personalized, and engaging. Social media serves as a platform for both individuals and businesses. Businesses utilize the platform to promote products and services alongside discerning potential and ideal customers. The increasing adoption of data-driven insights in marketing and personalized user experiences is expected to drive AI market growth to $2.2 billion by 2023 [3], with a CAGR of 28.3%. Therefore, user data security and user privacy are crucial aspects not to be overlooked as we progress towards a largely data-driven society.
Consider the emergence of deepfakes, a concerning development fueled by the content readily available on social media. Public authorities are increasingly urging social media platforms to enforce regulations rigorously. There is a growing emphasis on extending existing data privacy acts to effectively govern the use of AI and, in particular, to address the proliferation of deepfakes across social media platforms [4].
Big Data plays a vital role in the development and sustenance of AI systems. Companies like Facebook use the data collected from users, which includes user information, screen time, and more to make personalized content and targeted ads for the user. Therefore, external companies seeking to promote themselves pay companies like Facebook to ensure the appropriate audience is addressed using targeted advertisements. This method promotes a monopolistic approach to data collection and ownership of the user data for a company i.e. Google, Meta, and Facebook as this method helps them to use their user data for monetized services. The companies do implement measures like depersonalization and the parties for whom the data is being used are also not given access to user data. However, this monopolistic approach to the data stored by a company could involve underlying issues like mass surveillance by unauthorized entities or other entities like government or federal agencies [5].
Reflecting on the 2013 Snowden Leaks, it was revealed that certain companies willingly furnished user data to American authorities. The leaked information exposed the American National Security Agency’s (NSA) access to data from several major U.S. corporations, raising questions about the legality of their surveillance activities. Concerns linger regarding potential agency involvement in activities of dubious legality, a fact not widely known. Compounding the issue, these agencies operate without the obligation to disclose how they utilize collected data, maintaining opacity in their practices.
Returning to the overarching concern of privacy, the extent to which users divulge personal data hinges on their posting habits and social media connections. Social media envisioned as a continually expanding platform for online social interaction, poses an escalating concern about user data privacy, given the easy accessibility and abundance of data within these networks.
User data on social media often comprises personal information, essentially serving as intentional customer input. However, as users willingly contribute their data to receive personalized content, the ambiguity surrounding the extent of data usage and collection raises pertinent concerns about user privacy.
It is crucial to scrutinize the methods employed for data collection, ensuring they do not infringe upon the user’s trust. The case of Clearview AI’s app, which extracts facial recognition data from publicly accessible websites, serves as a poignant example. This practice not only raises concerns about forgotten customer data but also underscores the broader issue of data privacy [6].
This scenario underscores the imperative for establishing appropriate and stringent methods, backed by legal practices, to protect user data. Striking a balance between utilizing data effectively and safeguarding user privacy necessitates a comprehensive approach to data collection. Users should be informed about how their data is collected, stored, and utilized. Additionally, providing users with control over their personal data becomes paramount, emphasizing the significance of cultivating informed and empowered users within the data collection landscape. As technology advances, it becomes increasingly urgent to fortify safeguards and practices that uphold the privacy rights of individuals in the digital age.
In conclusion, the intricate marriage between social media and Artificial Intelligence, while bringing about unprecedented connectivity, personalization and convenience, has cast a shadow over the sanctity of user privacy. The revelations stemming from the 2013 Snowden Leaks and instances like Clearview AI’s data gathering underscore the urgent need for a reassessment of data collection practices and the implementation of robust legal frameworks.
As users willingly contribute personal information, often referred to as intentional customer input, they find themselves navigating an ambiguous landscape where the extent of data usage remains unclear. The emergence of deepfakes further heightens concerns, emphasizing the pressing need for stringent regulations.
The blog has explored the delicate balance required to preserve user privacy in an era where personalization thrives on user data. It is imperative to ensure that data collection methods remain transparent, ethical, and within legal bounds. Users should be empowered with knowledge about how their data is utilized, stored, and protected.
As we move forward into a future where the symbiosis between social media and AI continues to evolve, the emphasis must shift towards cultivating informed and empowered users. Striking this balance will not only protect individual privacy but also foster a digital landscape where innovation and ethical considerations coexist harmoniously. It is a call to action for users, regulatory bodies, and tech companies alike to collaboratively shape a digital future that respects the fundamental right to privacy in the age of technological advancement.
- Artificial intelligence risks to privacy demand urgent action – Bachelet | OHCHR
- The Anatomy of Mega-breaches: An Analysis of the Top 100 largest Data Breaches of the Past 15+ Years
- Unleashing the Power of AI in Social Media: A Complete Guide
- AI-powered deepfakes rise in 2023; concerns of its impact on privacy
- Artificial intelligence: dangers to privacy and democracy
- Artificial Intelligence for Marketing Management


