Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly growing field that is transforming our world in profound ways. While AI has the potential to improve many aspects of our lives, the increasing use also raises both ethical and societal questions about the negative impact of AI. In the context of social media and casino’s, AI can negatively influence us. Gambling and social media businesses are similar, both in the methods they use to attract and keep users and the habit-forming nature of the experiences in their products. “The business model of social media is addiction,” said Senator Sasse after the hearing of Facebook’s co-founder Mark Zuckenberg. This business model is similar to the business model of casino’s. The algorithms for these practices are designed to be addictive by manipulating user’s behaviour and emotions. We argue the addictive nature of algorithms created for social media and gambling and the negative consequences attached to this.
Social Media
Social media addiction is an addiction that is becoming more and more prevalent in our society today. Chamath Paliphapitiya, a former Vice President of User Growth at Facebook refers to social media platforms leveraging our neurological build-up in the same way cocaine and slot machines do. He said: “I feel tremendous guilt. The short-term, dopamine-driven feedback loops that we have created are destroying how society works”. Dopamine, often called the ‘happy hormone’, is the primary driver of the brain’s reward system; it spikes when we experience something pleasurable. Successful social interactions are an evolutionary advantage. For instance, more social animals can form alliances with each other, so the whole population stays stronger in terms of numbers. Therefore, due to this evolutionary advantage, these successful social interactions trigger dopamine release in our brain. Additionally, this reinforces the association between action and reward, motivating us to repeat this behaviour. Social media platforms keep us connected to unlimited amounts of constant social interactions. Algorithms are designed with techniques such as variable reinforcement, (providing rewards are random intervals), creating a sense of urgency (notifying users of a new message or update) and establishing habits (making the platform a routine part of the user’s day). Furthermore, by constantly monitoring its users’ online behaviour, collecting the data and also manipulating what the user sees online, the algorithms are keeping the users addictive to the social media platform. This phenomenon is also known as surveillance capitalism. While surveillance capitalism provides benefits, such as personal advertising and improved online experiences, it also raises some serious privacy concerns. The massive amounts of personal data collected can be vulnerable to hacking, misuse and exploitation.
Gambling

In her brilliant book “Addiction by design: Machine Gambling in Las Vegas” Natasha Dow Schüll outlines how the gambling industry tries to maximise the engagement, and thus profit, of machine gambling. This book, published in 2014, shows the first steps of how algorithms are implemented in slot machines. One way algorithms are implemented is by making slot machines work faster or slower, depending on the user. Some gamblers are more engaged when clicking the button quickly and constantly, while others want to play slower. Slot machines can learn and adjust the speed of play, for example by skipping certain animations or making the animations faster. This adjustment can then keep gamblers in their rhythm, thus keeping the player maximally engaged to the slot machine for as long as possible. Another way algorithms are used in gambling is by personalising the way the player wins and loses, for example, a risk-averse person will win 50 cents for every €3 they lose, while these numbers are made far higher for someone who likes risk more. Algorithms identify the risk-tolerance of the player and adjust the game based on the person playing. This creates a personalized experience that is designed specifically to keep the current player gambling. This constantly increasing level of engagement leads players to lose more money and makes it easier for players to get into the zone, a trance-like state where gamblers are fully engaged with the machine, and nothing else but the machine seems to exist for the players. In her book, Schüll tells the story of players in the zone not even noticing fire alarms or medical emergencies right next to them. According to Schüll, this feeling of pure engagement is something gamblers chase even more than winning, and this effect can be made much stronger by using AI to get the machines to adjust to get each player into this zone.
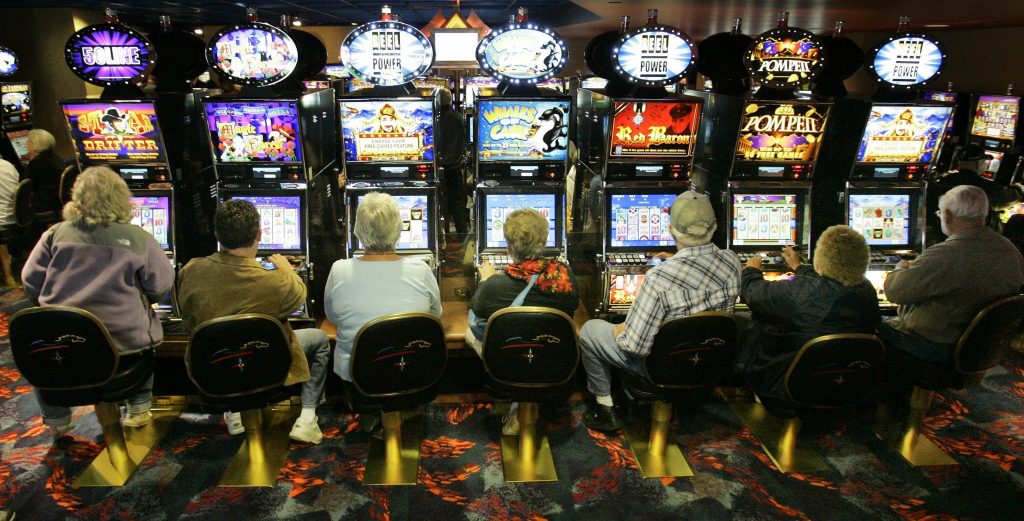

“Smart” gambling machines make players lose more money, and wholly engage players to a level that was not possible before. Chasing the feeling of ‘the zone’ and trying to make back lost money are some of the primary causes of addiction to slot machines. Causes that are made far more prevalent by the usage of AI.
Thankfully, AI can also help to combat problem gambling. Recent research has shown that algorithms can be used to predict whether people will self-report as a “Problem Gambler”, using data the casino has. This could help to identify and help these people before their gambling habits become uncontrollable. However, these algorithms only start detecting the problem gamblers when they already show problematic gambling behaviours, instead of before the gamblers start having problems. So a much better way of preventing these problems would be by not using AI to enhance gambling, as this can lead to far more problematic gambling, rather than by trying to detect problematic gamblers as they become problematic.
Consequences
Addictions caused by AI algorithms are becoming more and more prevalent in our society today. According to a study in China, 7.1 percent of the population in Asia is addicted to the internet, a figure which includes 24 million children in China. In other parts of the world, the estimation of the prevalence of internet addiction ranges from 7.9 to 25.2 % among adolescents. Worldwide, it is estimated that 210 million people suffer from social media addiction. With regards to the gambling machines driven by algorithms, a Yale study found that 2-7 % of youths develop a gambling disorder, compared with about 1% of adults. There are some serious consequences tied to addiction caused by AI. One of the most notable is mental disorders. These mental disorders include low self-esteem, impulsiveness, poor sleep, mood disorders, depression and suicide. There is a strong correlation found between mental health, quality of life and the level of internet addiction. For gambling addiction, the consequences also include financial and legal problems.
Conclusion
AI is a powerful tool that can enlarge or create new problems. The way AI can personalise and create habits and dopamine rewards for people can give many a better experience. However, it can also create huge problems for others, such as the ability of AI to facilitate addiction. This is already visible in practices such as social media and gambling. Therefore, we have to be aware of the negative consequences of AI and act before AI turns us into addicts.


