
When it comes to artificial intelligence, there are many different viewpoints and interpretations of what AI is and what it entails. AI encompasses a wide spectrum of technologies. This has had a transformative effect on what we can do with computers today. AI is used widely in many sectors namely, Healthcare, Banking and Finance, Entertainment, Marketing, Manufacturing, and so on. We are now witnessing some of the most significant advances in artificial intelligence in history. It has risen to prominence as the next big thing in technology, influencing the future of practically every sector. Virtual digital assistants(Alexa and Siri), in particular, with whom we contact on a daily basis for both minor and large tasks. Starting with the applications like virtual assistants, self-driving cars, and autonomous weapons, AI is progressing rapidly.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) is the present mechanism behind these applications, which indicates that these robots are only good at one or a few closely related jobs. People are currently attempting to reach the next level of artificial intelligence, in which machines can think and act similarly to humans (also known as Artificial General Intelligence(AGI)). It will help achieve remarkable progress in a variety of sectors, including genetics, healthcare, logistics, and many more. It can be applied to practically any field that has data and wants to take benefit of it, as it is mostly utilized for discovering patterns in data. It will aid us in our quest to comprehend the fascinating human mind, opening up several possibilities such as bettering education, gaining a better knowledge of brain illnesses, and learning how to reprogram our habits (our autopilot programs), among others.

“Artificial intelligence is the future, not only for Russia but for all humankind. It comes with colossal opportunities, but also threats that are difficult to predict. Whoever becomes the leader in this sphere will become the ruler of the world,” Russian President Vladimir Putin.
A new Cold War is looming, but this time it’s over artificial intelligence instead of nuclear weapons. The United States, China, and Europe are currently the leading players in AI development however more research is carried out in US and China. Although the EU is lagging behind, it continues to provide talent to the other two countries. According to a report from the Center for Data Innovation, the United States is currently leading the race, but it will not be long until China takes the lead. This is owing to the fact that collecting personal data is more practical, whereas the US government goes to great lengths to preserve residents’ privacy, particularly when it comes to data. Apart from the race between developed countries, tech companies are acquiring AI startups in an attempt to take the lead in AI. Besides this, tech companies are employing research methods in AI to stay ahead of the race. For instance, the business Meta, formerly known as Facebook, has announced the AI Research SuperCluster (RSC), which is said to be one of the world’s fastest AI supercomputers and will assist develop the metaverse by accelerating AI research.
Despite the fact that AI offers plenty of exciting possibilities, it also poses a serious threat to humanity, society, and the environment. Unemployment, wealth inequalities, dominating humans, reliance on technology, data abuse, autonomous weaponry, and cybercrime are the most common challenges. AI has come a long way in the previous decade, but a number of technological obstacles remain due to a variety of factors out of which power is the main obstacle. Is the fact that AI is slowing down due to technological constraints a good thing or a bad thing? Let’s say it’s a good thing, keeping in mind that we don’t fully understand AI’s capabilities. Before AI reaches its full potential, we need regulations in place to mitigate all the risks it could bring.
”The world hasn’t had that many technologies that are both promising and dangerous — you know, we had nuclear energy and nuclear weapons” – Bill Gates.
Bill Gates: Artificial intelligence ‘both promising and dangerous’ (cnbc.com)
In recent years, we’ve seen AI specialists frequently stress the importance of AI regulation. The occurrences detailed above serve as examples of why it is critical to have regulations in place. They were, without a doubt, eye-openers for the government, prompting it to reconsider current legislation or enact new ones.
The Cambridge Analytica Scandal, in which Cambridge Analytica acquired data from 50 million Facebook users without their knowledge or consent. This corporation had a big impact on the 2016 US presidential election and the Brexit referendum, which sent shockwaves around the world. It did, without a doubt, give many of us a fresh perspective on the digital world. This served as a wake-up call for the government to enact new legislation or reassess existing laws to ensure the security and privacy of users’ data. The General Data Protection Regulation, which replaced the Data Protection Act of 1995, is considered the gold standard around the world, strengthening your right to data protection. Killer robots, AI’s impact on the US presidential election, and Brexit are only a few instances of the threats AI poses to mankind and democracy, implying that AI regulation should receive more attention in order to prevent technology behemoths from acquiring worldwide control. Countries across the world are devising so many regulations with respect to Artificial Intelligence. Recently, the European Union suggested a set of AI regulations that, if broken, could result in substantial fines, while the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) issued a warning that it might hold corporations accountable for spreading bias or inequity using AI.
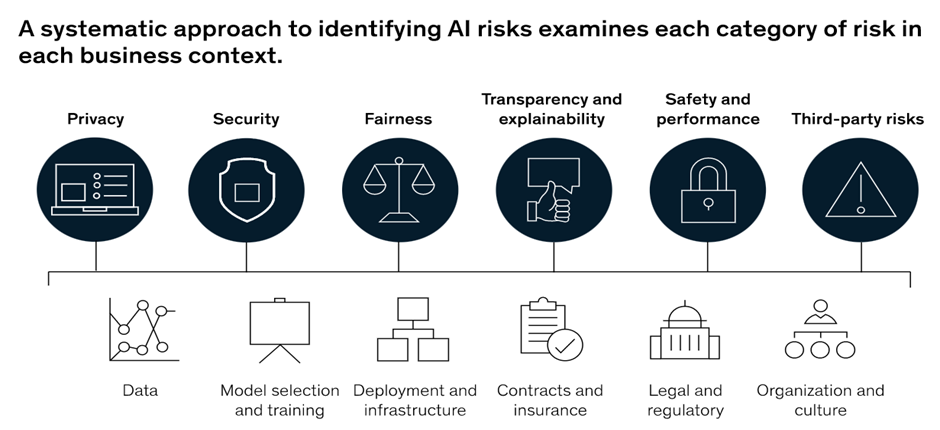
Before enacting new legislation, it is critical to consider the potential dangers and understand the motivations. As stated in the Mckinsey company article, utilize a framework to map risk categories against potential business settings and assess them.
Marina Gorbis, executive director of the Institute for the Future, said, “Without significant changes in our political economy and data governance regimes [AI] is likely to create greater economic inequalities, more surveillance and more programmed and non-human-centric interactions. Every time we program our environments, we end up programming ourselves and our interactions. Humans have to become more standardized, removing serendipity and ambiguity from our interactions. And this ambiguity and complexity is what is the essence of being human.”
https://www.aigency.com/2019/01/artificial-intelligence-in-2030/
Lawmaking must keep up with AI breakthroughs, ensuring that the law is kept up to date with new AI discoveries. In our perspective, law development in the field of artificial intelligence should take into account the wide range of uses of AI. For example, legislation that applies to a self-driving automobile may not make sense when applied to other sectors.
“On Artificial Intelligence, trust is a must, not a nice to have. With these landmark rules, the EU is spearheading the development of new global norms to make sure AI can be trusted. By setting the standards, we can pave the way to ethical technology worldwide and ensure that the EU remains competitive along the way. Future-proof and innovation-friendly, our rules will intervene where strictly needed: when the safety and fundamental rights of EU citizens are at stake.”Margrethe Vestager, Executive Vice-President for a Europe fit for the Digital Age.
https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_21_1682
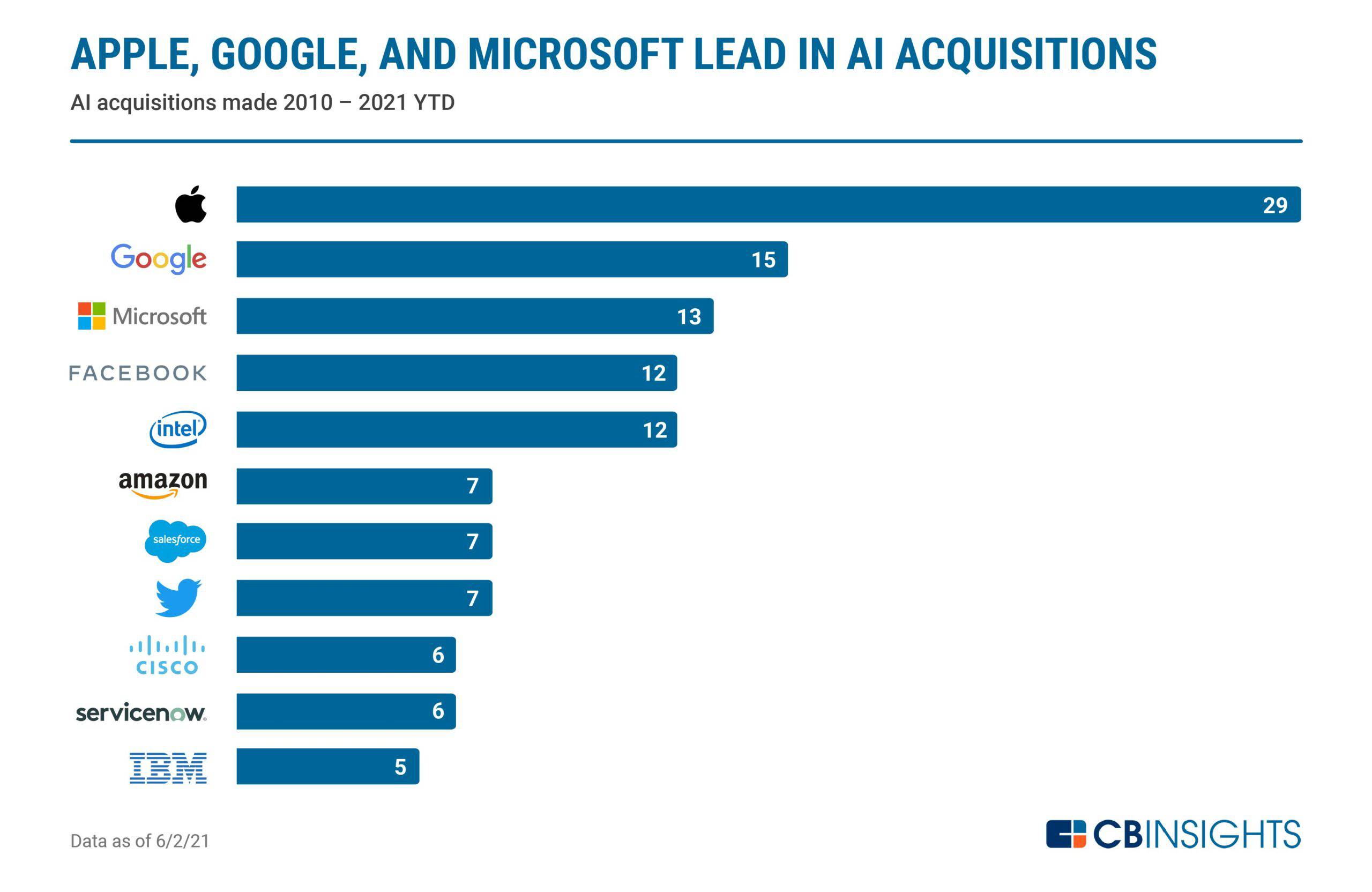
Although AI experts keep insisting that regulations are needed on AI, there are a lot of challenges in achieving it. Because AI is a diverse field, it is unquestionably tough for lawmakers to accomplish their jobs. More study is needed to develop legislation for the numerous industries that use AI. Regardless, tech behemoths such as Microsoft, Google, Facebook, Tesla, IBM, and Amazon should be active in educating the public about the advancements of AI. Public sectors should conduct research in collaboration with these tech behemoths. The fact that the United States is the headquarters of these organizations gives up a plethora of possibilities. Different countries use different approaches to developing Artificial Intelligence rules.
Countries such as China, on the other hand, take a different approach to this issue. Interestingly, ethics, privacy, and security have various meanings around the world. In China, for example, facial recognition technology – biometric computer applications that automatically identify an individual from a database of digital photos – is commonplace. However, proponents of facial recognition in the United States frequently claim that the technology should be reserved for the most dangerous concerns, such as violent crimes, terrorist threats, and human trafficking. The Chinese government is accused of utilizing facial recognition technology to commit atrocities against Uyghur Muslims, relying on it to carry out “the world’s largest mass incarceration of a minority group today.“
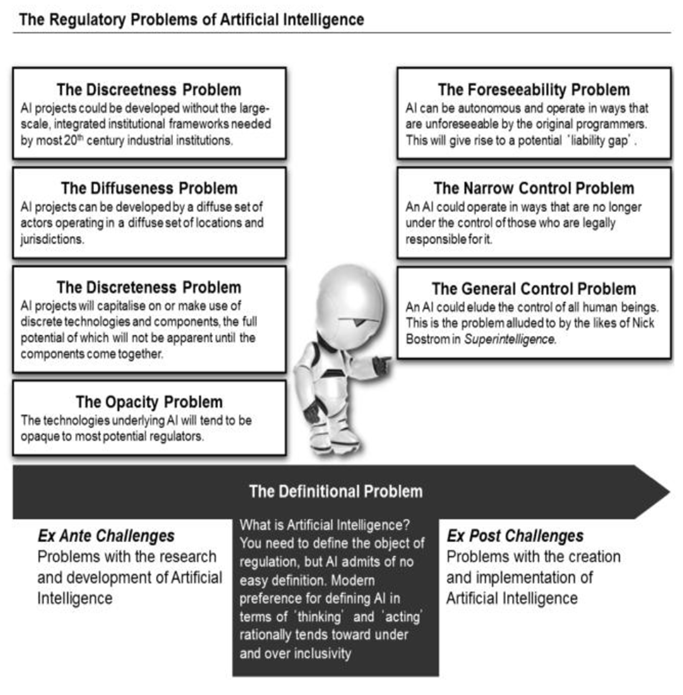
We’d want to touch on some of the issues that have arisen in the regulation of Artificial Intelligence. Each of the issues listed below appears to be substantial, and any regulatory system would have to deal with them. The diffuseness and opacity issues are the most problematic. The diffuseness issue shows that there is a need for worldwide collaboration in AI governance, but previous efforts at global coordination do not inspire trust (e.g. climate change; nuclear proliferation). The opacity issue is also serious, and it is likely to be exacerbated by the increasing use (and demand for) AI in regulatory decision-making.
We would want to believe that the AI legislation would lead us along a path that is beneficial to society. On the contrary, there are events that raise the question of whether regulations are sufficient to prevent the unexpected repercussions of AI to persons, companies, or society The latest cyber-attack on Ukraine’s government’s official websites is another example of technology exploitation that has gained international attention.
“Aggressive cyber operations are tools that can be used before bullets and missiles fly,” says John Hultquist, head of intelligence for the cybersecurity firm Mandiant
https://www.technologyreview.com/2022/01/21/1043980/how-a-russian-cyberwar-in-ukraine-could-ripple-out-globally/
These incidents demonstrate the negative impacts of AI when it falls into the wrong hands. There is no guarantee that such attacks will stop. We cannot forget the 2017 cyber-attacks NotPetya and WannaCry, which damaged the entire world and cost billions of dollars. In the case of the Cambridge Analytica incident, the data breach occurred despite the fact that there was a data protection statute in existence.
The danger of AI is much greater than the danger of nuclear warheads by a lot. AI is far more dangerous than nukes. – Elon Musk
https://www.boldbusiness.com/digital/elon-musks-neuralink-brain-chips/
On the one hand, western countries such as the United States and Europe are enacting legislation that is nearly identical in terms of preventing the negative effects of AI. However, the regulations developed in China are diametrically opposed to those of the United States and Europe, allowing China to reach new heights in Artificial Intelligence. Because AI approaches differ among countries, the possibilities of an immoral incident occurring are relatively high.
To recapitulate, we believe that Artificial Intelligence laws will shield society from the unexpected consequences of AI. It is undoubtedly challenging to regulate a rapidly expanding technology. Multiple studies on all industries that use AI must be conducted in order for the rules to be more effective. We believe that the only way to escape the AI catastrophe is to regulate artificial intelligence. However, because the regulations are developed by multiple countries and there is no international agreement in place, such as the Paris Agreement or the Non-Proliferation Treaty, binding all governments throughout the world to follow the same set of regulations, it may not be totally successful.

In our opinion, a public entity, such as the United Nations, should be appointed to oversee the development of AI and to implement restrictions based on the findings. For the rules to be effective, all of the nations that have pioneered AI must reach an agreement. As previously noted, the legal systems of Western countries are vastly different from those of China, Russia, and North Korea. Otherwise, these governments risk misusing the technology for their own gain, regardless of the outcome. On the contrary, there have been occasions in the past where present regulations were broken, posing a threat to democracy. These occurrences not only highlight the significance of international agreements but also raise the question of whether rules will fulfill their goal of preventing the exploitation of artificial intelligence and rescuing society.


